What is a retrospective

"The single most important practice in Scrum is the retrospective because it allows the team to learn, improve, and adapt its process." ¹
What is a Retrospective?
A retrospective is a structured and efficient meeting where a team gathers to analyze challenges, explore ideas, and develop actionable solutions to improve their work process.
Collaboration naturally brings about misunderstandings, challenges, and occasional dissatisfaction. The greatest obstacle is not encountering these challenges but failing to address them effectively. Without a structured reflection process, teams risk repeating mistakes, leading to stagnation and reduced learning. Retrospectives provide a framework for continuous improvement, ensuring that teams identify roadblocks, refine workflows, and evolve together.
Who Can Benefit from Retrospectives?
Retrospectives are not exclusive to Agile teams or leaders—they are valuable for any team striving to enhance collaboration and efficiency. Whether you're part of a development team, a marketing group, or a project-based organization, retrospectives help foster a culture of growth, problem-solving, and shared learning.
What Does a Typical Retrospective Look Like?
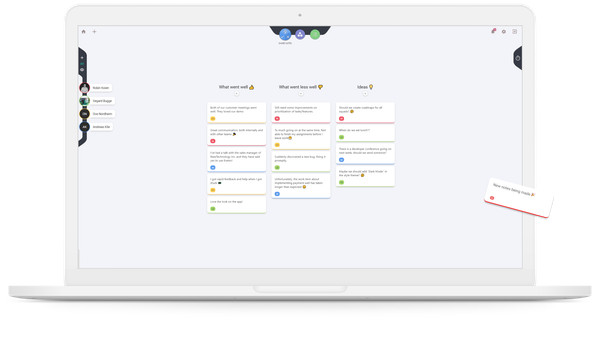
Most teams conduct retrospectives every two weeks, dedicating 1-2 hours to reflect and improve. Below is an example of a structured retrospective process:
1. Reflect and Take Notes
Gather your team and allocate 5-10 minutes for individual reflection on the previous work period.
The Three Questions Method
- What worked well? – Identify successes and elements worth continuing.
- What didn’t work well? – Highlight challenges and areas needing improvement.
- Puzzles and Ideas – Express uncertainties, ask questions, and suggest new approaches.
2. Present and Share Insights
Each team member presents their notes, ensuring a shared understanding of both wins and challenges. This phase fosters open communication, allowing team members to align on key takeaways from the previous work cycle.
3. Discuss, Find Solutions, and Define Action Items
- Engage in a collaborative discussion to identify potential solutions.
- Encourage brainstorming to drive innovative approaches to recurring challenges.
- Create clear, actionable tasks that team members can implement.
- Assign ownership and set deadlines to ensure follow-through on improvement efforts.
- Visualize tasks using tools like digital boards or workflow trackers to reinforce accountability.
4. Implement Changes and Improve
A retrospective is only valuable if the insights lead to action. After the session, teams must commit to executing agreed-upon action items to achieve meaningful improvements. Completing these actions leads to enhanced collaboration, refined workflows, and overall team efficiency.
Keep in mind that this is a foundational retrospective structure—many different techniques and approaches can be tailored to fit your team's needs.
Transform Your Team with Retrospectives
Regular retrospectives empower teams to proactively solve problems, refine processes, and continuously improve. When teams make reflection and adaptation a habit, they enhance productivity, foster trust, and achieve long-term success.
📢 Follow us on LinkedIn for expert insights on boosting team performance!
References:
- Project Management Institute and Agile Alliance, Agile Practice Guide, Project Management Institute, September 2017.